Tanace Organics Pvt. Ltd

Natural Dyes: The Eco-Friendly Choice for Going Green with Color.
In recent years, there has been a growing movement towards sustainable and eco-friendly practices in various industries, including fashion and textiles. One of the ways this is being achieved is through the use of organic dyes in the production of fabrics and textiles. Natural dyes are made from renewable resources such as plants, fruits, and vegetables, and do not contain harmful chemicals or synthetic materials that are commonly found in conventional synthetic dyes.
This makes them a more environmentally friendly choice for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint and support sustainable practices. In this essay, we will explore the benefits of using organic dyes, as well as the challenges and limitations associated with their use in the fashion and textile industry.
Table of Contents
What is Natural Dye?
They have been used for thousands of years to color fabrics and textiles, and are still used today in many cultures around the world. Unlike synthetic dyes, which are made from petrochemicals and other harmful materials, natural dyes are made from renewable resources and do not contain toxic chemicals that can harm the environment or human health.
The process of making eco-friendly dyes involves extracting color from plant materials through a process of boiling, soaking, or fermenting. This color is then transferred to the fabric or textile through a process of immersion or application. organic dyes produce a range of colors, from earthy tones to bright hues, depending on the type of plant or material used, as well as the mordant (a substance used to fix the dye) and the method of application.
While organic dyes are generally considered to be more environmentally friendly than synthetic dyes, there are still some environmental concerns associated with their use.

Advantage Of Natural Dye
There are several advantage of Natural Dye:
- Environment Friendly
- Biodegradability
- Non-Toxic
- Health Benefit
- Promote Traditional and cultural Practice
Environment Friendly
Natural dyes are made from plants, nutrients and insects, which are completely renewable resources and do not harm the environment.
One of the best things about natural dyes is that they are environmentally friendly. Unlike synthetic dyes, which are often made from non-renewable materials and contain chemicals, organic dyes come from renewable materials such as plants, grapes, fruits and vegetables. This means that non-renewable materials have less of an impact on the environment, as they do not cause destruction or air and water pollution.
Also, the manufacture of dyes is often more labor-intensive than synthetic dyes. This is because organic dyes can be extracted by simple processes such as boiling, soaking or fermentation, whereas synthetic dyes require complex reactions that use a lot of energy.
Biodegradability
Natural dyes are biodegradable, meaning they break down easily without harming the environment.
Another advantage of natural colors is that they are biodegradable. Unlike synthetic dyes, which can take centuries to break down and release harmful chemicals into the environment in the process, vegetable dyes are biodegradable and pose no threat to the environment or human health. This means that textiles and fabrics dyed with organic dyes can be disposed of without the influence of non-biodegradable waste.
Non-Toxic
Natural dyes do not contain harmful chemicals such as heavy metals that can cause health problems for humans and animals.
Non-toxic natural dyes are a great alternative to synthetic dyes that contain harmful chemicals such as heavy metals. These toxins not only threaten human and animal health, but also pollute the water and soil and harm the environment. In contrast, organic dyes are made from plants, minerals, and insects, which are renewable resources and do not contain harmful chemicals. They are also biodegradable, meaning they break down easily in the environment without harming them. The use of non-toxic chemicals creates a healthy, safe environment for all and supports a culture that benefits people and the planet.
Health Benefit
There are also many health benefits associated with natural dyes over synthetic dyes. Many synthetic dyes contain toxic chemicals such as benzidine and formaldehyde, which have been linked to many health problems, including cancer, skin irritation and respiratory problems. In contrast, organic dyes do not contain these harmful chemicals, making them a safer option for those who use or wear dyed textiles and fabrics.
It also has beneficial properties that can be beneficial to health, such as some vegetable dyes, antioxidants, and antibiotics. For example, it has been shown that turmeric, a natural dye commonly used in India, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, while root dye, another natural dye, has antibacterial properties.
Promote Traditional and cultural Practice
The use of natural dyes supports the fabric dyeing tradition and culture, preserves local knowledge and supports local communities.
The use of natural dyes can promote fabric dyeing culture and tradition, preserve local knowledge and support local communities. Natural dyeing techniques have been used for thousands of years and are an important part of many cultures around the world. By promoting natural dyeing, we can help preserve traditional techniques and support the livelihoods of local artisans who have been practicing them for generations.
This also helps support culture and tradition, as organic dyes are often produced locally and reduce the carbon footprint associated with transporting and manufacturing synthetic products. By using natural colors, we can celebrate culture and support sustainable development in communities around the world.

Sources Of Natural Dye
Natural dyes can be obtained from many sources, including plants, animals and food. Some natural sources of dyes include indigo, root dye, turmeric, and henna. Animals include cochineal and shellfish, which can produce red and purple dyes. Minerals such as ocher, iron oxide and copper create earthy tones. Different parts of the plant can produce different colors, such as roots, leaves, and flowers.
Each natural color source produces a unique color palette that can vary based on factors such as the age of the plant or method of extraction. Here are some sources of the Dye:
- Plant Based Dye
- Animal Based Dye
- Minerals Based Dye
Plant Based Dye
Vegetable-based dyes are the most widely used organic dyes. They come from many parts of plants, including roots, leaves, flowers and bark. Some common vegetable dyes include indigo, root dye, turmeric, and onion peel. Each herb produces a different color that varies depending on the part of the plant used, the time it was harvested, and the extraction process.
Animal Based Dye
There are various types of animal dyes, including those derived from insects, mollusks, and crustaceans. These dyes are not used as vegetable dyes and are often difficult to maintain. An example of an animal-based dye is cochineal, which comes from insects that feed on cactus plants. Cochineal produces a bright red color and has been used in traditional textiles for centuries.
Minerals Based Dye
Mineral-based paints are obtained from food and are used less frequently than plant-based paints. Dyes can produce many colors such as red, yellow and brown. An example of a mineral-based paint is ocher, an earth pigment that has been used for thousands of years to create a variety of colors. Mineral-based paints are often combined with other types of natural paints to achieve colors and effects.
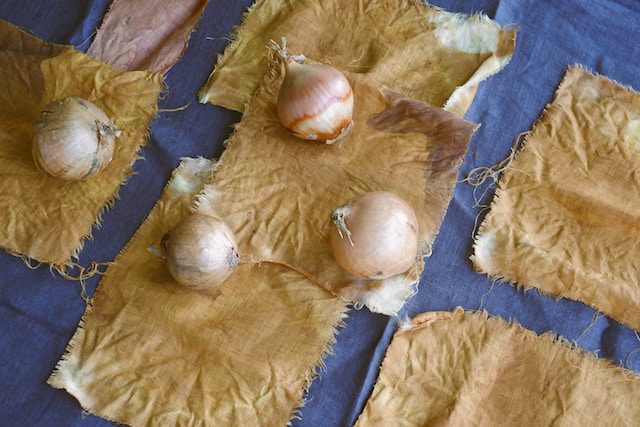

History Of Natural Dye
The history of natural dye usage dates back thousands of years, encompassing a global journey of discovery and innovation. Early civilizations like the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans employed plant and mineral sources to color textiles, adding vibrant hues to their garments. As trade routes expanded, the exchange of dye-bearing materials between cultures led to the spread of dyeing techniques and color knowledge.
In ancient Asia, particularly in regions such as India and China, natural dyeing reached remarkable heights. The Indian subcontinent, for instance, boasted an array of botanical sources like indigo, turmeric, and madder that were used to create intricate and diverse color palettes. The famous indigo dye, extracted from the leaves of indigofera plants, was highly sought after and played a significant role in global trade. Similarly, Chinese civilizations mastered techniques like resist dyeing and discovered vibrant red dyes from sources like safflower.
During the Renaissance, Europe experienced a fascination with exotic colors and textiles, leading to the exploration of new dye sources. The quest for novel hues prompted endeavors to find alternatives to expensive imported dyes like indigo. The quest ultimately played a pivotal role in sparking interest in chemistry and the development of synthetic dyes in the late 19th century.
While the advent of synthetic dyes revolutionized the textile industry, it also raised concerns about environmental impact and health risks. This reignited interest in natural dyes as a sustainable and safer alternative. In recent decades, the revival of traditional dyeing techniques and a growing emphasis on eco-friendly practices have led to a resurgence of interest in natural dyes among artisans, designers, and conscious consumers, thereby weaving a historical thread of color innovation through the fabric of time.
Challenges Using in Natural Dyes
Although there are many benefits to using natural colors, there are also some problems with their use:
- Color Consistency
- Cost
- Limited Color Range
- Time Consuming Process
- Environmental Impact
Color Consistency
vegetable dyes are less predictable than synthetic dyes, and colors can vary based on factors such as plant type, season, and extraction method. Getting the same color can be difficult. One of the main problems with working with natural colors is that they can produce color changes that are difficult to control. This is because the color of organic dyes can be affected by factors such as the type of plant or material, when it was collected, and the extraction process. Therefore, it will be difficult to achieve the same color when natural colors are used.
Cost
vegetable dyes can be more expensive than synthetic dyes because raw materials are more expensive and the dyeing process is longer. Another difficulty with using natural colors is that they can be more expensive than synthetic colors. This is because the production of organic dyes can be more work than synthetic ones and may require more assistance. Additionally, some vegetable dyes can be difficult to stabilize, increasing their cost.
Limited Color Range
Although eco-friendly dyes provide a unique and versatile palette, the color range is more limited than synthetic dyes. The availability of organic dyes is also difficult, especially in areas where traditional dyeing techniques are replaced by synthetic dyes. This can make it difficult for artisans and manufacturers to obtain reliable natural dye products, limiting their ability to produce sustainable and quality products. In addition, the increasing demand for vegetable dyes in recent years has led to problems with deforestation and land use as producers seek new sources of vegetable dyes.
Time Consuming Process
Creating natural dyes is a complex process that requires careful planning and attention to detail. Painting materials must be collected, cleaned and prepared in a special way to ensure the quality of the color. The painting process can take hours or days, depending on the color desired and the material being painted. In order to achieve the desired result, the fabric must be kept in the dye bath for a long time, and the temperature and pH of the bath must be carefully monitored. While this process can take a long time, it also allows for greater thinking and awareness about fashion, which can lead to greater satisfaction with the final product.
Environmental Impact
Although eco-friendly dyes are generally considered more environmentally friendly than synthetic dyes, their use can affect the environment if not managed properly. If not managed sustainably, mass production can lead to deforestation, land degradation and water pollution. In addition, the process of obtaining dyes from natural conditions requires a significant amount of water, energy and land use.
However, natural dyeing can have positive effects on the environment, such as promoting renewable agriculture and reducing the carbon emissions associated with the production and transportation of synthetic materials. By promoting culture and ethics, we can help reduce the negative environmental impact of eco-friendly dyes and contribute to a more sustainable fashion industry.
Synthetic Dye and their Hazards
Synthetic dyes are the most widely used dyes in the textile industry. Although they are reasonably priced and available in a variety of colors, they also have some dangers associated with their use:
- Negative Environmental Impact of Synthetic Dye
- Negative Impact on Human Health
- Comparison between Natural and synthetic dyes
Negative Environmental Impact of Synthetic Dye
Synthetic dyes have a huge impact on the environment. The production of synthetic paints is related to the use of petrochemicals, a non-renewable resource that contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. In addition, the discharge of synthetic materials into rivers and other water sources can cause serious pollution and cause waterborne diseases. Chemicals used in synthetic products also pollute the soil and air, causing environmental problems.
Negative Impact on Human health
Synthetic dyes have also been associated with many health problems. The chemicals used in synthetic paints can cause skin irritation, allergies and respiratory problems in people who use or wear products containing synthetic materials. Additionally, some synthetic dyes have been linked to more serious health problems, including cancer and birth defects. These health risks are of particular concern to those working in the textile industry or near textile mills that use synthetic materials.
Comparison between Natural and Synthetic dye
Natural dyes are generally biodegradable and do not contain harmful chemicals that can harm the environment or human health. They are also renewable and can be obtained from plants, animals and food. Also, vegetable dyes can create very beautiful and unique colors that cannot be reproduced with synthetic dyes. However, eco-friendly dyes have some disadvantages, including the potential for discoloration and higher costs. However, the environmental and health benefits of using natural colors make them a better and more environmentally friendly option than synthetic colors.
Conclusion
As a result, natural dyes have a number of better synthetic dyes. They are environmentally friendly, biodegradable and harmless to humans. They also provide unique and beautiful colors that cannot be replicated with synthetic dyes. Considering the negative effects of synthetic dyes on the environment and human health, it is important to encourage the use of eco-friendly dyes. By using eco-friendly dyes we can promote sustainable and eco-friendly work, encourage the use of renewable materials and protect our health and the environment.
As consumers, we can make decisions by choosing products made with eco-friendly dyes and supporting companies that use good practices and the environment. We can also educate ourselves and others about the benefits of natural colors and the risks of synthetic colors. Working together, we can help create a healthier future for ourselves and the planet.
Frequently Asked Question:-
- How can I dye my clothes naturally at home?
Ans- To dye clothes naturally at home, you can start by selecting plant-based sources like onion skins, turmeric, or beetroot for desired colors. Prepare the fabric by washing and soaking it in a fixative like salt or vinegar. Simmer the chosen dye material in water, strain the dye liquid, and bring it to a gentle boil. Add the fabric and simmer until the desired color is achieved. Rinse the fabric, allow it to dry, and avoid excessive washing to preserve the color.
- How do you make homemade dye?
Ans- To make homemade dye, choose a plant-based source like berries, spinach, or flowers for the desired color. Chop or crush the chosen material and place it in a pot. Cover with water and simmer for about an hour, periodically stirring. Strain the liquid into a container, and it’s ready for use as a natural dye for fabrics, yarn, or even paper. Remember to adjust the quantity of dye material and simmering time for varying shades.
- How was dye made in medieval times?
Ans- In medieval times, dye was typically made from natural sources such as plants, minerals, and insects. Different parts of plants like roots, leaves, and flowers were collected and processed. The desired color was extracted through techniques like boiling, fermenting, or crushing the plant material. These pigments were then combined with various mordants, such as alum or iron, to fix the color to fabrics. The dyeing process was often labor-intensive and required a deep understanding of plants, minerals, and traditional techniques.
- How can I dye my fabric black without dye?
Ans- Dyeing fabric black without using traditional dyes can be challenging, but you can try a method called “eco-printing.” This involves placing leaves or botanical materials onto the fabric, wrapping it tightly, and then steaming or boiling it. The tannins and natural pigments from the plants can create intricate patterns and shades, including darker tones that resemble black. Keep in mind that the results can vary and may not achieve a true black color, but rather a range of grays and deep tones. Experimentation with different plants and techniques will help you achieve the desired effect.
- What are synthetic dyes used in?
Ans- Synthetic dyes are utilized across numerous industries for coloring various products. They find extensive use in the textile and apparel sector, where they provide a wide spectrum of vibrant and long-lasting colors to fabrics and clothing. These dyes are also employed in the cosmetics and personal care industry for creating shades in products like makeup and hair dyes. Additionally, synthetic dyes are integrated into plastics, packaging materials, and food products to enhance aesthetics and visual appeal, as well as in sectors like printing, paper manufacturing, and even pharmaceuticals for coloring purposes.